A Farmer’s Guide to Making Organic Manures at Home
Organic manure is an essential component for enriching the
soil and promoting healthy crops. It’s a sustainable way to
reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers, improve soil
structure, and enhance microbial activity. Here’s a guide to
making organic manure at home:
Understanding Organic Manure
Organic manure is made from natural materials like
decomposed plant matter, animal waste, and agricultural
residues. It provides essential nutrients to the soil,
improving its fertility over time.
Types of Organic Manure
-
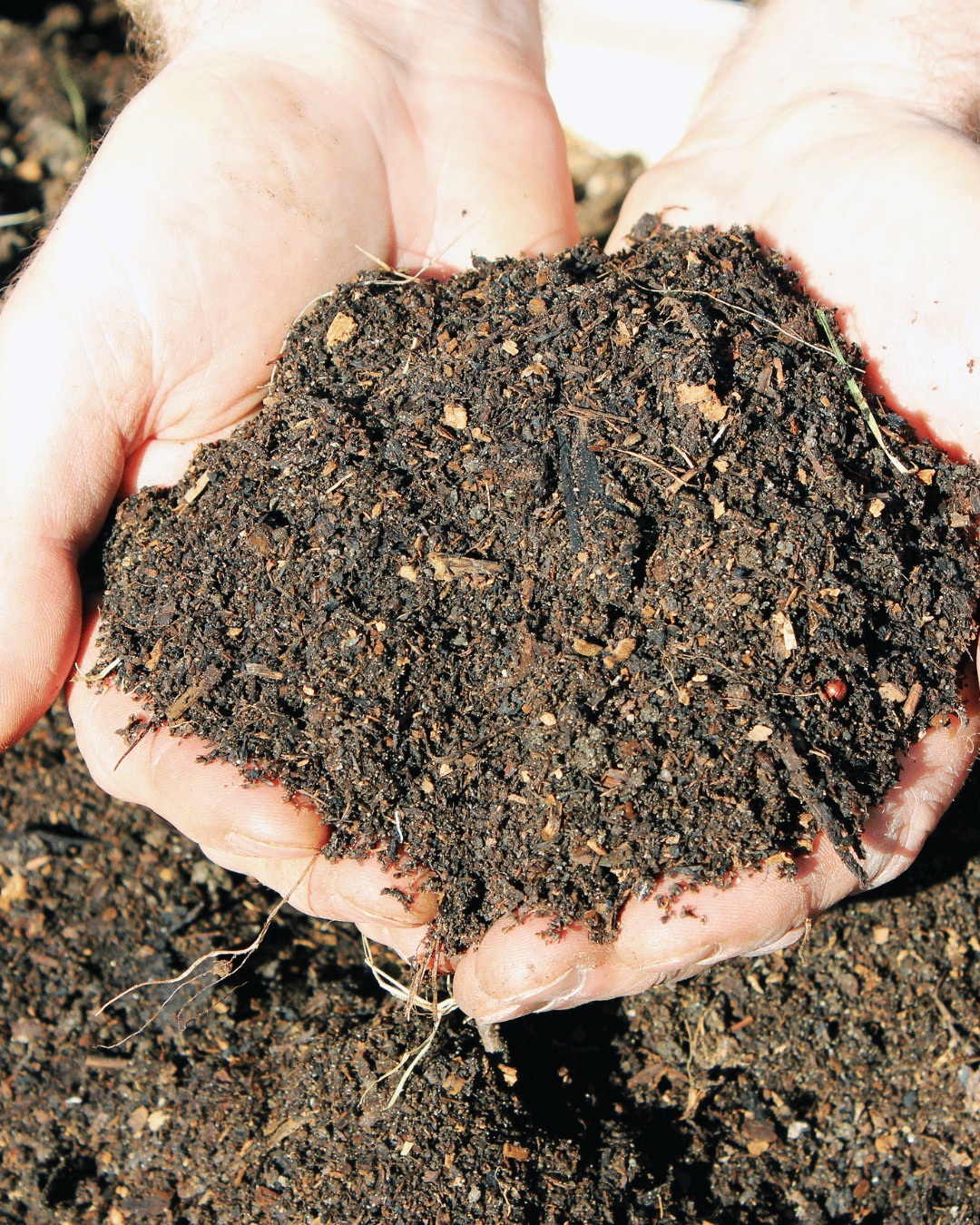
Compost: Made
from kitchen scraps, dry leaves, and garden waste.
-
Vermicompost:
Produced using earthworms to break down organic matter.
-
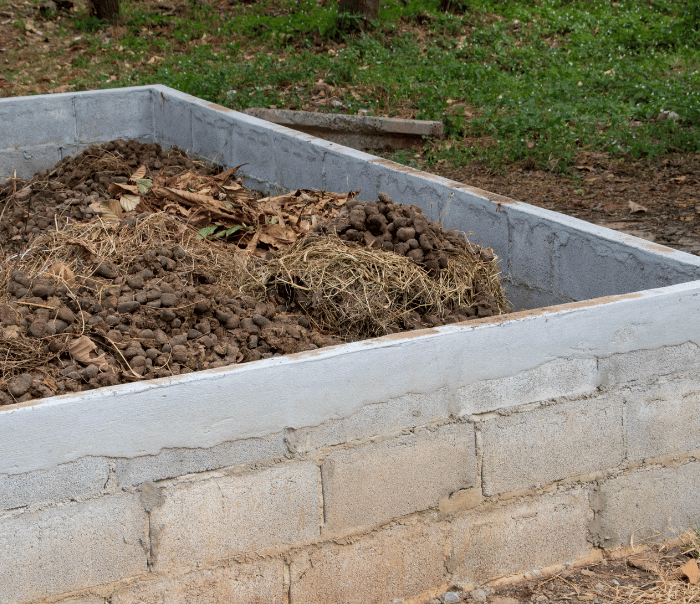
Farmyard Manure (FYM):
Composed of cow dung, urine, and bedding materials.
-
Green Manure:
Fresh plant material plowed into the soil to improve
fertility.
Steps to Make Compost at Home
-
Collect Waste Materials:
Use fruit peels, vegetable scraps, dried leaves, and
farm residues.
-
Layering:
Alternate between dry and wet organic matter to balance
carbon and nitrogen.
-
Aeration: Turn
the pile regularly to allow oxygen flow.
-
Moisture Maintenance:
Keep the pile moist but not too wet.
-
Maturation:
Allow 4–6 weeks for decomposition before using it in the
fields.
Benefits of Using Organic Manure
-
Enriches the soil with essential nutrients for healthier crops.
-
Improves soil structure, reducing water runoff and wastage.
-
Encourages beneficial microbes that aid root development.
-
Strengthens soil structure, minimizing erosion and degradation.
-
Slowly releases nutrients, ensuring long-term soil nourishment.
-
Reduces reliance on chemical fertilizers, benefiting the environment.
-
Enhances plant growth, leading to better harvests.
-
Revitalizes degraded soils, making them more productive.
-
Minimizes groundwater contamination and chemical runoff.
-
Reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, saving money in the long run.
Conclusion
By making organic manure at home, farmers can maintain soil
health and ensure a chemical-free, sustainable approach to
agriculture.